The violin is not only an ancient instrument but also one of the world’s most versatile and universal musical instruments. It is popular worldwide for its variety of musical styles and expressive tones. Violin has a very interesting long history.
Ancient to Modern Violin History Timeline
How Did The Violin Get Its Name?
The word “violin” derives from the Medieval Latin word “vitula”. It means “string instrument”. It is thought that the word “vitula” comes from the word “vitulari” which means “to be joyful” or “to make merry.”. The Roman goddess of joy is also called “Vitula”.
However, some alternative etymologists say that the word vitula means “a calf.” As the strings of the instrument were made from calf gut, this theory suggests that vitula designated the string instrument. This etymology of the word violin indicates that violin as a musical instrument has a long history.
The violin is also known as a fiddle which has a hollow wooden body. This wooden string instrument is the smallest as well as the highest-pitched instrument in the violin family.
Most violins have four strings that are played by drawing a bow across the strings. Though it became popular in the 16th century, the development of modern violin evolved with other stringed musical instruments. Here we would like to discuss a short history of the violin.
Violin History Facts

The ancient forms of early violins don’t exist today. The history of the ancient violin is mainly inferred from the era of ancient paintings that represents violins. The ancient origin of the violin was found on the island of Sri Lanka back to 5000 BCE. It is known as the oldest ancestor of the violin and called “Ravanastron”. This had one string that is about 22-inch long. This string spanned three octaves that could produce a similar tonal range of contemporary violin.
However, different stringed instruments can be found throughout the ancient world. The pear-shaped lira was one of the oldest ancestors of the violin.

It was found in Europe during the early ninth century. It was played in an upright position and bowed. The lira that had seven strings was also an instrument for street poets.
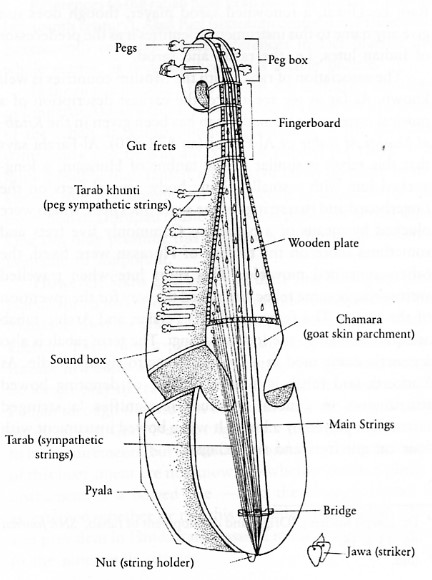
The Arabian rabab and the rebec are also considered the ancestors of the violin. The Arabian rabab was a two-string instrument that was usually played upright. This Arabian fiddle was introduced to western Europe in the 11th century. On the other hand, the rebec was mainly used in the Middle East during the 10th century. It was held under the chin while playing and it had three strings. Later it appeared in Spain between the 11th and 13th centuries. The rebec was played widely in Spain and France in the fifteenth century. A bowed stringed instrument known as the fiddle appeared in Europe near the end of the middle ages.
The French vielle was another ancestor of violin. It was widely used between the 13th and 15th centuries. Usually, it was used to accompany the singing and dancing performance. It is considered as one of the earliest evolutions of the rebec.

It had three to five strings and was very popular among the Medieval troubadours. The vielle and lira both are considered ancestors to the fiddle. These were made their way to court musicians in the 15th and 16th centuries.
Viola is considered the earliest form of a contemporary violin. Famous composer Monteverdi used the viola in his symphonic compositions in the early 17th century. Viola was a member of the viola da braccio family. The viola da braccio or viole da braccio is the name for the first formal family of string instruments. These instruments were held in the arms while played. The viola da gamba family was another stringed instrument and this was held between the knees when played.
Viol was another similar-looking instrument that was used in the fourteenth century. The violin and the viol actually coexisted in the Baroque period. But viol did not have an f-shaped soundhole. Rather it had a C-shaped or some other decorative shape soundhole.
The viol differs from the violin as it has six, seven, or more strings. It tuned in fourths and a fretted fingerboard. Usually, it had a relatively thick body with a sloping shoulder shape. Viol was found in various sizes.
Various stringed instruments including violin have a long history in folk music. Especially earlier forms of violins were played in folk music in many countries. The tenor violin is occasionally referred to as the viola popularly known from the 16th century through the 18th century.
Thus, from the Chinese erhu to the Greek kithara different ancestors of the violin widely appeared in the ancient period.
Where Did The Violin Originate
Most historians agree that the modern violin was developed in Italy. A mural in the Saronno Cathedral is the most prominent example of an old violin.

This representation of the three-string violin is dated to around 1535. This Cathedral is located in the Lombardy region of Italy. Lombardy is also home to the cities of Brescia and Cremona. This region is full of maple and spruce trees that are particularly well-suited for string-instrument like the violin. These two types of wood are still favorite by violin makers and were available in the Lombardy region. So, this place was the first center of master luthiers.
Master-craftsman Andrea Amati was born in 1510. His renowned work made Cremona of Italy the center for violin making in Europe.

He built a violin workshop in 1539. This workshop of Cremona became one of the premier musical workshops in Europe. Amati’s workshop was built in his house and it was a family venture that remained in his family’s possession for 200 years.

The French queen regent Catherine de Médicis asked Amati to make a variety of string instruments in the early 1560s. The queen required these musical instruments for the Royal Ensemble. It is thought that the basic forms and design of modern violin were established with the scale of this work. Amati created a wooden soundbox with two f-shaped apertures. This instrument was tuned to perfect fifths. The four strings stretched along the instrument’s neck were perfectly tightened with pegs and established the basic form of the modern violin.

Amati made a violin for the French king Charles IX in 1564. It is one of the oldest surviving examples of a modern violin which is stored in the Ashmolean Museum of England. On the contrary, Amati’s “Kurz” violin is also considered as one of the oldest violins that may have been part of a royal wedding gift in 1559. This “Kurz” violin is on display at New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art.

Amati shared the secrets of his craft with his two sons, Girolamo and Antonio. Later the dynasty extended to a third generation. Girolamo’s son Nicolò became the maestro of the two most celebrated violin makers named Andrea Guarneri and Antonio Stradivari.
Master violin maker Antonio Stradivari was born in 1644. He was famous for his excellent quality violin that is made in his Cremona workshop. His excellently crafted instruments became treasures and highly valued for the acoustics.
The violin’s majestic sound continued to expand throughout the centuries. Gradually the violin became an important instrument of modern classical music during the 17th century. At first, violins were used for dance music. But in the 17th century, it replaced the “viol” in chamber music. Many famous composers and musicians incorporated the magical tunes and perfect harmony of violin for greater prominence in the orchestra. Gradually it became an essential instrument in the orchestra. The violin’s majestic sound proved that it has the ability to evoke almost any mood such as sweet, sad, playful, or somber. The Italian composer Claudio Monteverdi introduced violins in the orchestra in 1607. Many renowned composers such as Mozart, Beethoven, Arnold Schoenberg, and Alban Berg wrote solo music for the violin in the 18th century. Antonio Vivaldi, Franz Joseph Haydn, and Niccolò Paganini continued to focus on the sounds of the strings and made violin more presentable to the music lovers. King Louis XIII of France also had a great contribution to establishing the violin as the central place in classical music.
How Has The Violin Changed Over Time
The first high-quality modern form of violins was crafted by the luthiers of Italy. Brescia and Cremona are the home to the world’s most famous luthiers like Giuseppe Guarneri, Antonio Stradivari, and the Amati family.
Andre Amati from Cremona and Gasparo di Bertolotti from Salon are the two earliest violin makers in recorded history. They both are from northern Italy and had a great contribution to establishing the perfect form of the modern violin. They excelled in the crafting of violins and became synonymous with the art of violin making. These two violin maker brands are still producing violin and are widely accepted by the violin players. The oldest violin that is in existence today is also built by Andre Amati.
Contemporary violins emerged in the early 16th century. The first standardized design was developed by Andrea Amati. He produced a large number of string instruments and popularized the f-curve as part of the violin’s design.
However, the shape and dimensions of the modern violins were standardized and slightly modified in the 19th century. The placement of the notches was set as a pointer so that the bridge can be installed appropriately.

In this way, the remaining s-curves of the violin gave way to the f-curve. The bridge height, lengthening of the neck and fingerboard also developed in the 19th century when the luthiers prioritized the comfortability of the violin players.
Besides Italians, there are many other contributors to shape and design bowed stringed instruments like the violin.
Frenchman François Tourte made a remarkable mark in 1786 to standardize the dimensions of the modern bow. He introduced intensive bowing techniques that allowed the violin players to keep more balanced.
Louis Spohr from German introduced the chin rest in 1820. The invention of the chin rest made the instrument easier to hold.
The violin makers tried to lengthen and tilted the neck and fingerboard in the 19th century so that it can increase the range of play.
The earlier violins are more deeply arched in the belly and back while the modern form the violins are shallower. Especially the innovations of Antonio Stradivari made the violin tone more melodious.
The last major changes in the modern violins’ design occurred in the 19th century. During this time, the bridge was heightened and the bass bar was thickened. It made the violin body flatter.
As a result, now violins are able to generate a brilliant and stronger tone compared to the intimate and delicate tone of the 18th century.
The engineer of the National Symphony Orchestra named Marshall Moss and William Bartley developed the first electronic violin in 1938.
This modern addition of the violin family is getting more popular in commercial performances like stage plays, and music festivals. This instrument has a solid body and it is intentionally made to be electrified with built-in pickups. Acoustic or Classical violin usually is made of a hollow structure that amplifies the vibrations of the strings. On the contrary, an electric violin must be connected to an amplifier to be heard.
Read our review articles
- 9 Best Cheap Violins That Produce Amazing Sound
- 9 Best Violins for Professionals [Modern + Classical]
- 9 Best Violins for Advanced Players in 2021
- 9 Best Violins For Beginners In 2021 [With Buying Guide]
- 9 Best Cheap Violins That Produce Amazing Sound
And it goes on…
The violin was widely recognized for its beautiful tone when it was introduced in its birthplace Italy. But later the beautiful majestic tone of the violin impressed the world. Different people of different places provided great contributions to the development of the violin. Though some progressive modification ultimately helped the evolution of this musical string instrument, the basic design of violins is still following the classical forms of violins. The earliest violin makers had determined the average proportions of an ideal violin in the 16th century and now the modified design of the modern violin allowed the violinist to play the finest tones.




it is helpful